Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability is a topic of growing importance in today's world. These elements are essential for a wide range of technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles to wind turbines. Yet, despite their importance, many people do not know much about them. This guide will provide you with the background Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability and the critical roles they play in our modern world.
Editor's Notes: Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability have published today date
Through our analysis, we have gathered the information and made Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability we put together this Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability guide to help you make the right decision.
There are a number of key differences between rare earth elements and other elements. First, rare earth elements are much less common than other elements. They make up only about 0.001% of the Earth's crust. Second, rare earth elements are often found in very small deposits. This makes them difficult to mine and process. Third, rare earth elements have unique chemical and physical properties. These properties make them essential for a wide range of technologies.
Rare earth elements are used in a variety of technologies, including:
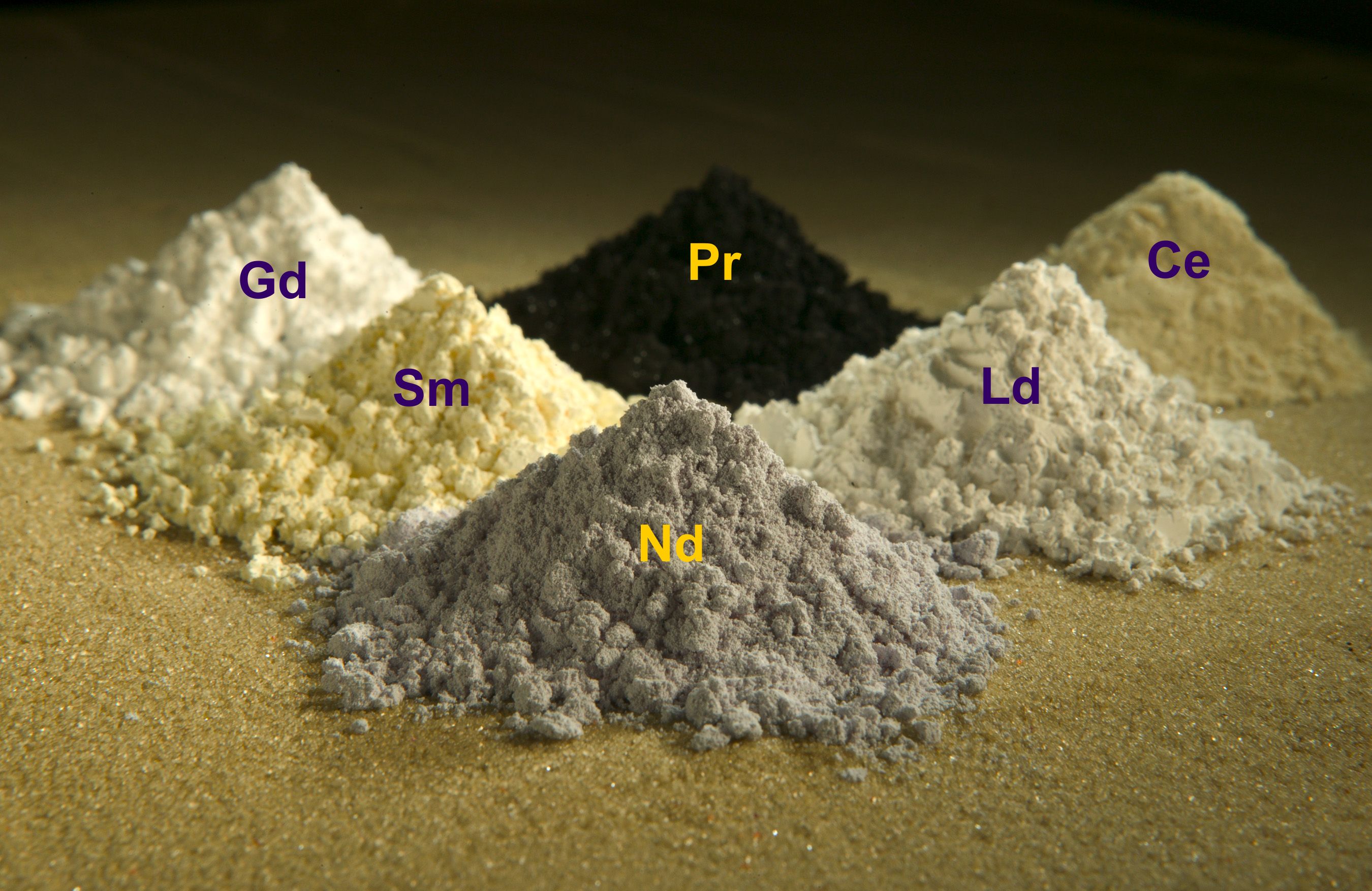

What’s So Rare About Rare Earth Elements? - Source acceleratingscience.com
FAQ
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions regarding rare earth elements, their significance in technology, and their impact on sustainability.
Question 1: What are rare earth elements and why are they important?
Rare earth elements are a group of 17 chemically similar metals essential for various technologies. They possess unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties crucial for products such as smartphones, electric vehicles, and wind turbines.

Rare Earth Elements: What Are They? Who Has Them? - IER - Source instituteforenergyresearch.org
Question 2: Are rare earth elements scarce as their name suggests?
Despite their name, rare earth elements are relatively abundant in the Earth's crust. However, their extraction and processing are complex and expensive, leading to their designation as 'critical' materials.
Question 3: How do rare earth elements impact sustainability?
The mining and processing of rare earth elements can have significant environmental consequences, including water pollution, soil erosion, and habitat loss. However, these elements are essential for developing sustainable technologies, such as renewable energy and energy-efficient devices.
Question 4: Is there enough supply of rare earth elements to meet future technological demands?
Meeting the increasing demand for rare earth elements requires sustainable mining practices, exploration of alternative sources, and recycling and recovery efforts. Collaboration among governments, industries, and research institutions is crucial for ensuring a secure supply chain.
Question 5: What are the potential alternatives to rare earth elements?
Research is ongoing to find substitutes or alternative materials that can replace or reduce the reliance on rare earth elements. However, many of these alternatives are still in the early stages of development.
Question 6: How can individuals contribute to sustainable use of rare earth elements?
Promoting responsible consumption of electronic devices, supporting recycling programs, and advocating for sustainable mining practices can help individuals contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of rare earth elements.
Understanding the critical role of rare earth elements while addressing sustainability concerns is essential for responsible use and future technological advancements.
Tips
Considering the critical role of rare earth elements (REEs) in modern technology and sustainability, it's essential to embrace sustainable practices: Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability
Tip 1: Promote Recycling and Recovery
Establish efficient recycling programs for electronic devices, magnets, and other REE-containing products. By recovering and reusing REEs, we reduce mining and environmental impacts.
Tip 2: Invest in Sustainable Extraction
Encourage research and development of environmentally friendly extraction techniques. Explore methods that minimize waste, reduce water consumption, and limit emissions.
Tip 3: Optimize REE Usage
Design technologies that use REEs efficiently. Explore alternative materials or innovative approaches to reduce the overall REE consumption.
Tip 4: Support Responsible Mining Practices
Promote and enforce strict mining regulations to minimize environmental and social impacts. Ensure responsible waste management, habitat conservation, and community engagement.
Tip 5: Educate and Raise Awareness
Increase public awareness about the importance of REEs and the need for responsible management. Encourage educational programs and initiatives.
By implementing these tips, we can foster sustainability, mitigate environmental concerns, and ensure the long-term availability of REEs for critical technologies.
Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability
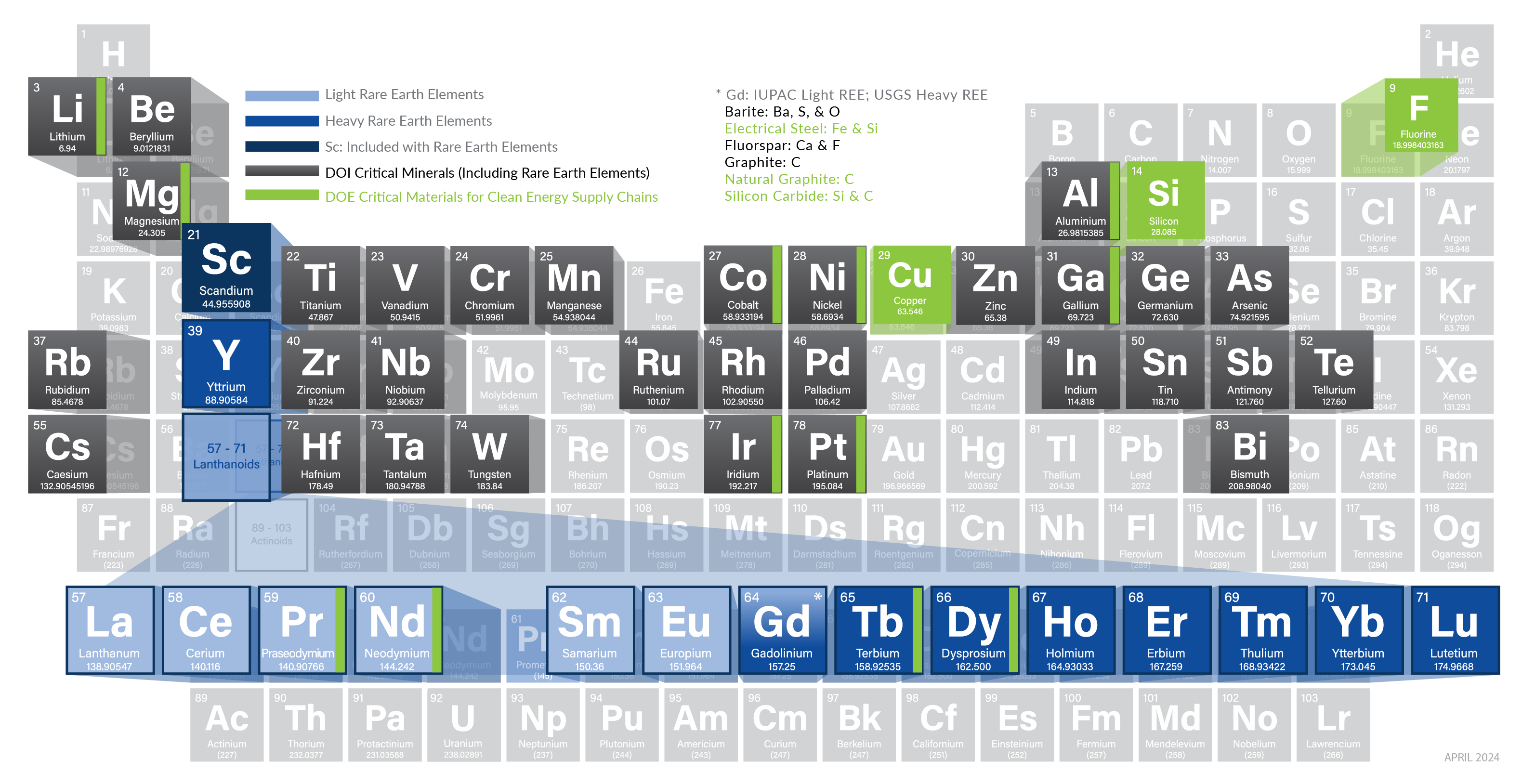
Rare Earth Elements – A Subset of Critical Minerals | netl.doe.gov - Source www.netl.doe.gov
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 elements that are essential for many modern technologies. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including electronics, magnets, and batteries. REEs are also critical for the development of clean energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines.
- Scarcity: REEs are relatively rare, and they are not evenly distributed around the world.
- Importance: REEs are essential for many modern technologies.
- Sustainability: REE mining can have negative environmental impacts.
- Demand: The demand for REEs is growing rapidly.
- Supply: The supply of REEs is limited.
- Price: The price of REEs is volatile.
The six key aspects of REEs discussed above are all interconnected. The scarcity of REEs makes them important, but it also makes them vulnerable to supply disruptions. The growing demand for REEs is putting pressure on the supply, and this is driving up the price. The environmental impacts of REE mining are also a concern, and this is leading to calls for more sustainable mining practices.
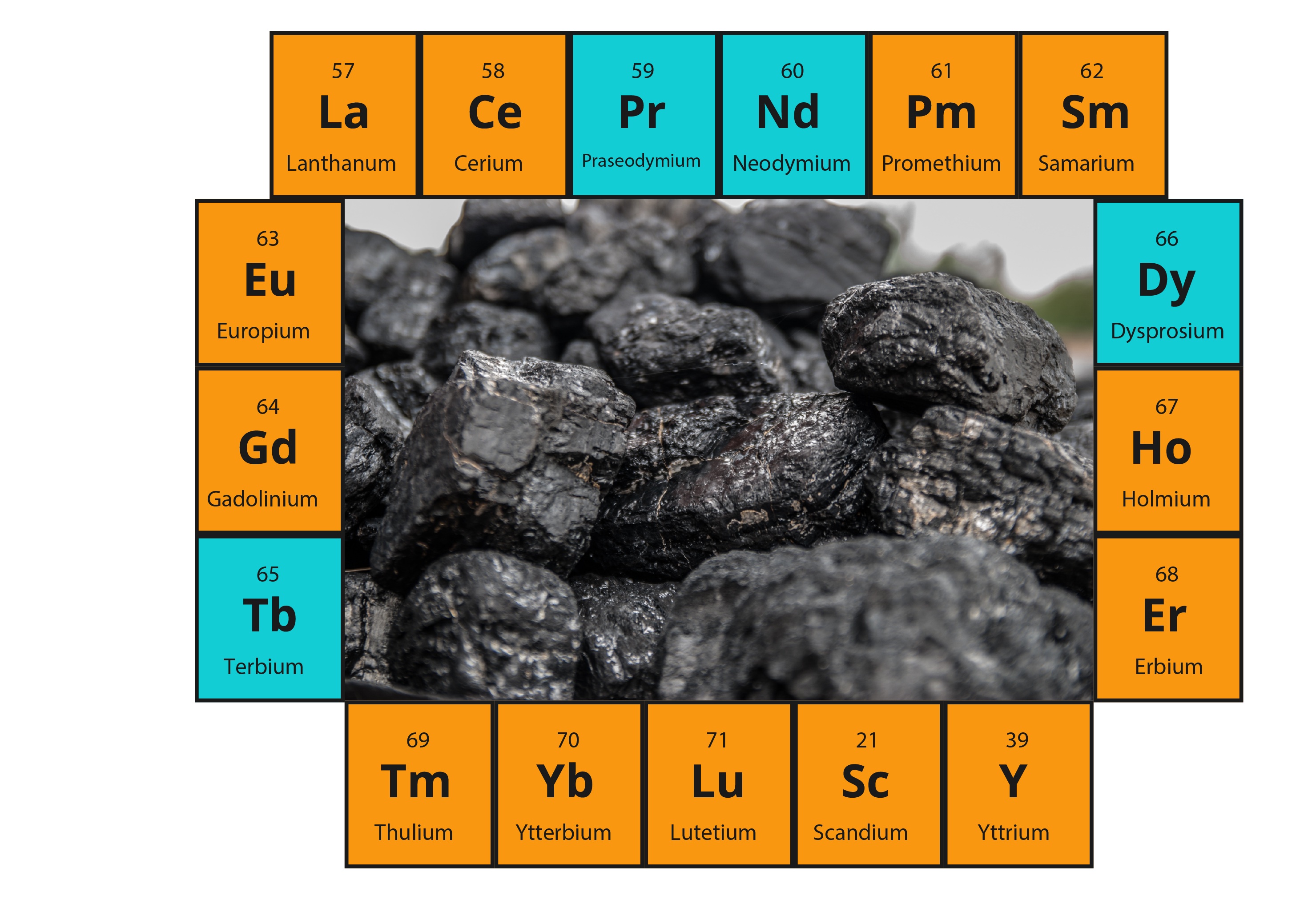
Carbon Ore, Rare Earth and Critical Minerals | Bureau of Economic Geology - Source www.beg.utexas.edu
Rare Earth Elements: Understanding Their Critical Role In Technology And Sustainability
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 elements that are essential to many modern technologies, including smartphones, computers, and electric vehicles. They are also used in a variety of other applications, such as lasers, magnets, and batteries. REEs are found in small amounts in the Earth's crust, and their mining and processing can have a significant environmental impact.
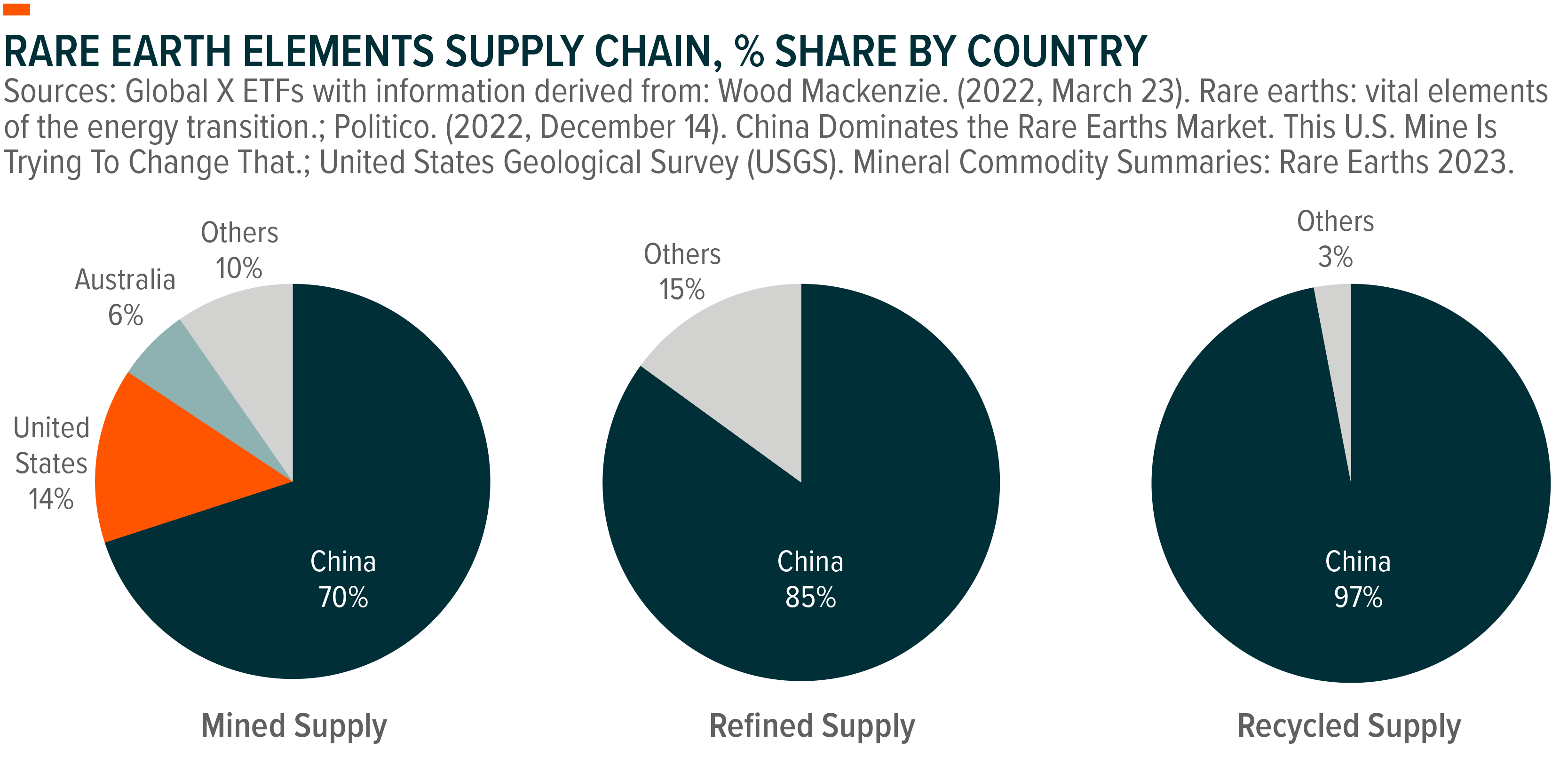
Rare Earth Elements, Explained - Global X ETFs - Australia - Source www.globalxetfs.com.au
The demand for REEs is growing rapidly, as more and more devices rely on them. This has led to concerns about the sustainability of the REE supply chain. In order to meet the growing demand for REEs, it is important to develop more sustainable mining and processing methods, as well as to recycle REEs from electronic waste.
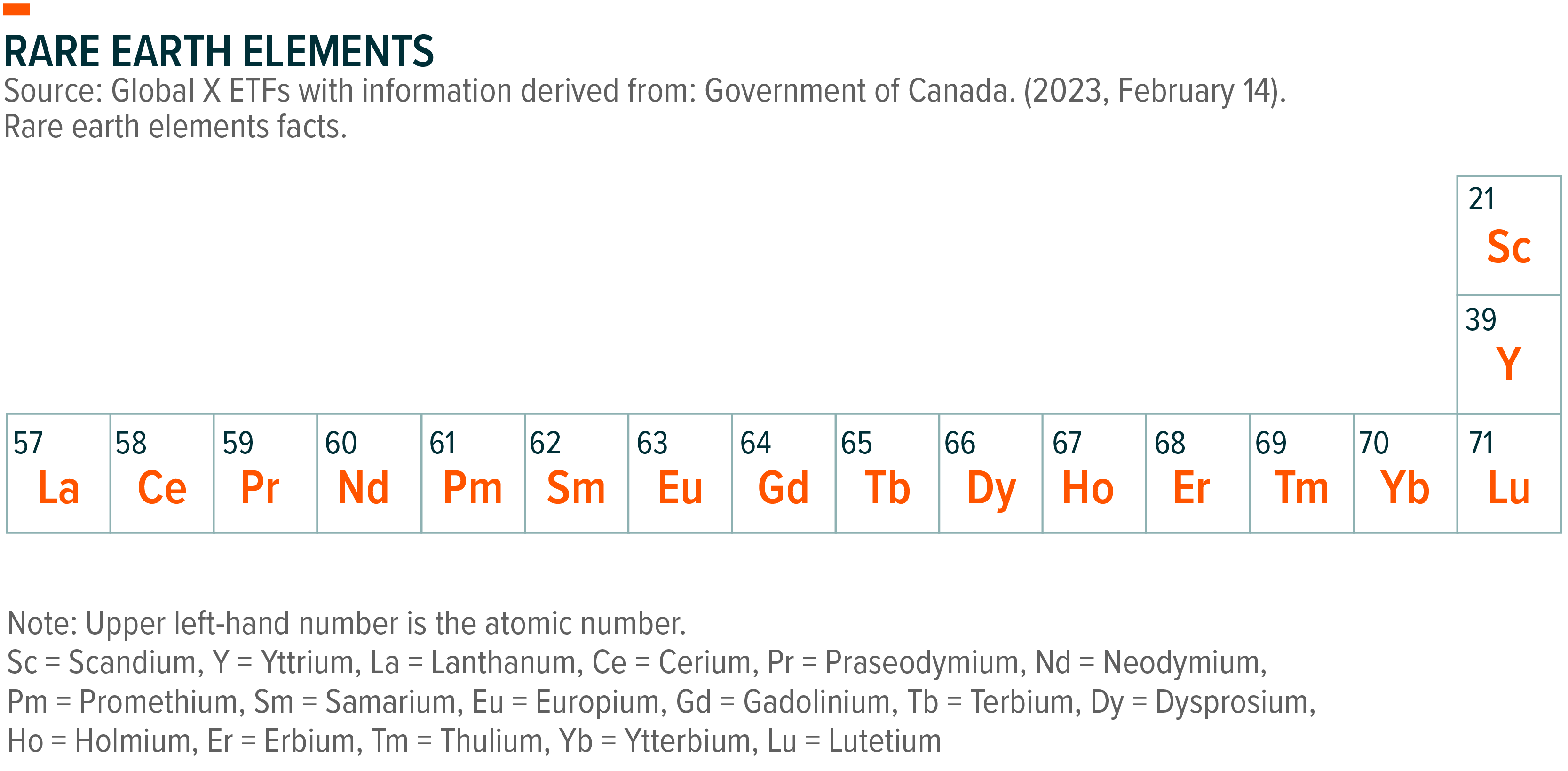
Rare Earth Elements, Explained - Global X ETFs - Australia - Source www.globalxetfs.com.au
The critical role that REEs play in technology and sustainability makes it essential to understand their properties and applications. By doing so, we can make informed choices about how to use these valuable resources in a way that minimizes their environmental impact.
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lanthanum | La | 57 | Batteries, magnets, alloys |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 | Catalysts, polishing agents, alloys |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 59 | Magnets, lasers, phosphors |
| Neodymium | Nd | 60 | Magnets, lasers, phosphors |
| Promethium | Pm | 61 | Radioactive tracer |
| Samarium | Sm | 62 | Magnets, lasers, phosphors |
| Europium | Eu | 63 | Phosphors, lasers, magnets |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | Phosphors, lasers, magnets |
| Terbium | Tb | 65 | Phosphors, lasers, magnets |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | Magnets, lasers, phosphors |
| Holmium | Ho | 67 | Magnets, lasers, phosphors |
| Erbium | Er | 68 | Lasers, phosphors, amplifiers |
| Thulium | Tm | 69 | Lasers, phosphors, amplifiers |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 70 | Lasers, phosphors, amplifiers |
| Lutetium | Lu | 71 | Phosphors, scintillators, alloys |



