RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment is a common infection of the lungs and airways caused by a virus. It can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in young children. RSV is spread through contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person, such as when they cough or sneeze.

Respiratory Syncytial Virus Symptoms - Family Care Centers Medical Groups - Source www.fccmg.com
Editor's Notes: RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment have published today date because this topic has a lot of concern about RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment.
Our team of experts has analyzed and dug into the information available about RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment, and we assembled this RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment guide to help you make informed decisions about your health.
Key Differences
| Characteristic | RSV |
|---|---|
| Symptoms | Runny nose, cough, fever, wheezing, difficulty breathing |
| Prevention | Wash hands frequently, avoid contact with sick people, cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze |
| Treatment | There is no specific treatment for RSV, but symptoms can be managed with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications |
Main Article Topics
- Symptoms of RSV
- Prevention of RSV
- Treatment of RSV
FAQ
This FAQ section provides comprehensive answers to frequently asked questions about Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), empowering individuals with essential knowledge and guidance.
Question 1: What are the common symptoms of RSV?
RSV typically manifests through respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, runny nose, and fever. These symptoms may resemble the common cold but can be more severe, especially in infants and young children.
Question 2: How is RSV spread?
RSV is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person or contact with surfaces contaminated with the virus.
Question 3: Who is at risk of severe RSV infection?
Infants, particularly those under six months old, premature babies, and individuals with underlying heart or lung conditions are at an increased risk of developing severe RSV infections.
Question 4: How can I prevent RSV infection?
Effective preventive measures include frequent hand washing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces. Vaccination against RSV is also recommended for certain high-risk groups.
Question 5: What are the treatment options for RSV?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for RSV. Supportive care, such as rest, pain relievers, and fluids, is the mainstay of treatment. In severe cases, hospitalization and oxygen therapy may be necessary.
Question 6: How long does RSV typically last?
The duration of RSV infection varies, typically lasting for several days to a week. However, symptoms may persist for a longer period in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Summary: RSV is a common respiratory virus that can cause mild to severe symptoms. Understanding the virus, its transmission, and preventive measures is crucial for minimizing the risk of infection. If you suspect RSV infection, seek medical attention promptly, especially for infants and high-risk individuals.
Transition: For further information on RSV, including prevention strategies, treatment options, and current research, navigate to the next article section.
Tips
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common and potentially serious respiratory infection that affects infants and young children. It can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, cough, runny nose, and difficulty breathing. While there is no specific cure for RSV, there are several things that can be done to prevent and treat the infection.
Tip 1: Wash your hands frequently.
One of the most important things you can do to prevent RSV is to wash your hands frequently with soap and water. This will help to remove the virus from your hands and prevent you from spreading it to others.
Tip 2: Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze.
When you cough or sneeze, cover your mouth and nose with a tissue. This will help to prevent the virus from spreading through the air.
Tip 3: Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
If you are sick, stay home from work or school to avoid spreading the virus to others. If you are healthy, avoid close contact with people who are sick.
Tip 4: Clean and disinfect surfaces.
Clean and disinfect surfaces that are frequently touched, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops. This will help to remove the virus from these surfaces and prevent it from spreading.
Tip 5: Get vaccinated against RSV.
There is a vaccine available to prevent RSV. The vaccine is recommended for all infants and young children. It is given in two doses, the first dose at 2 months of age and the second dose at 4 months of age.
Summary
By following these tips, you can help to prevent and treat RSV. If you have any questions about RSV, please see a doctor for more information.
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common and contagious virus that affects the respiratory tract. It is a major cause of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in infants and young children worldwide. RSV infection can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and in some cases, can lead to hospitalization. Understanding its symptoms, prevention, and treatment strategies is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of children.
- Symptoms: Runny nose, cough, fever, wheezing
- Transmission: Droplets from infected individuals
- Prevention: Hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, immunization
- Diagnosis: Clinical examination, laboratory testing (e.g., PCR)
- Treatment: Supportive care (e.g., fluids, oxygen), antiviral medication (in severe cases)
- Complications: Pneumonia, bronchiolitis, hospitalization
RSV infection is particularly concerning in infants and young children, as they are more susceptible to severe complications. Prevention measures, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding contact with infected individuals, are vital in reducing RSV transmission. Immunization with the RSV vaccine is also recommended for high-risk infants to provide additional protection. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent serious complications. Understanding these key aspects of RSV infection empowers individuals to take preventive measures, seek timely medical attention, and contribute to reducing the burden of RSV on the healthcare system and the community.

Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Concept Stock Photo - Image - Source www.dreamstime.com
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): Symptoms, Prevention, And Treatment
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus that can cause infection in the lungs and respiratory tract. It is the most common cause of bronchiolitis and pneumonia in infants and young children. RSV can also cause serious illness in adults, especially those with weakened immune systems or chronic lung conditions. Symptoms of RSV infection include fever, cough, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and decreased appetite. RSV is spread through contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person. The virus can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
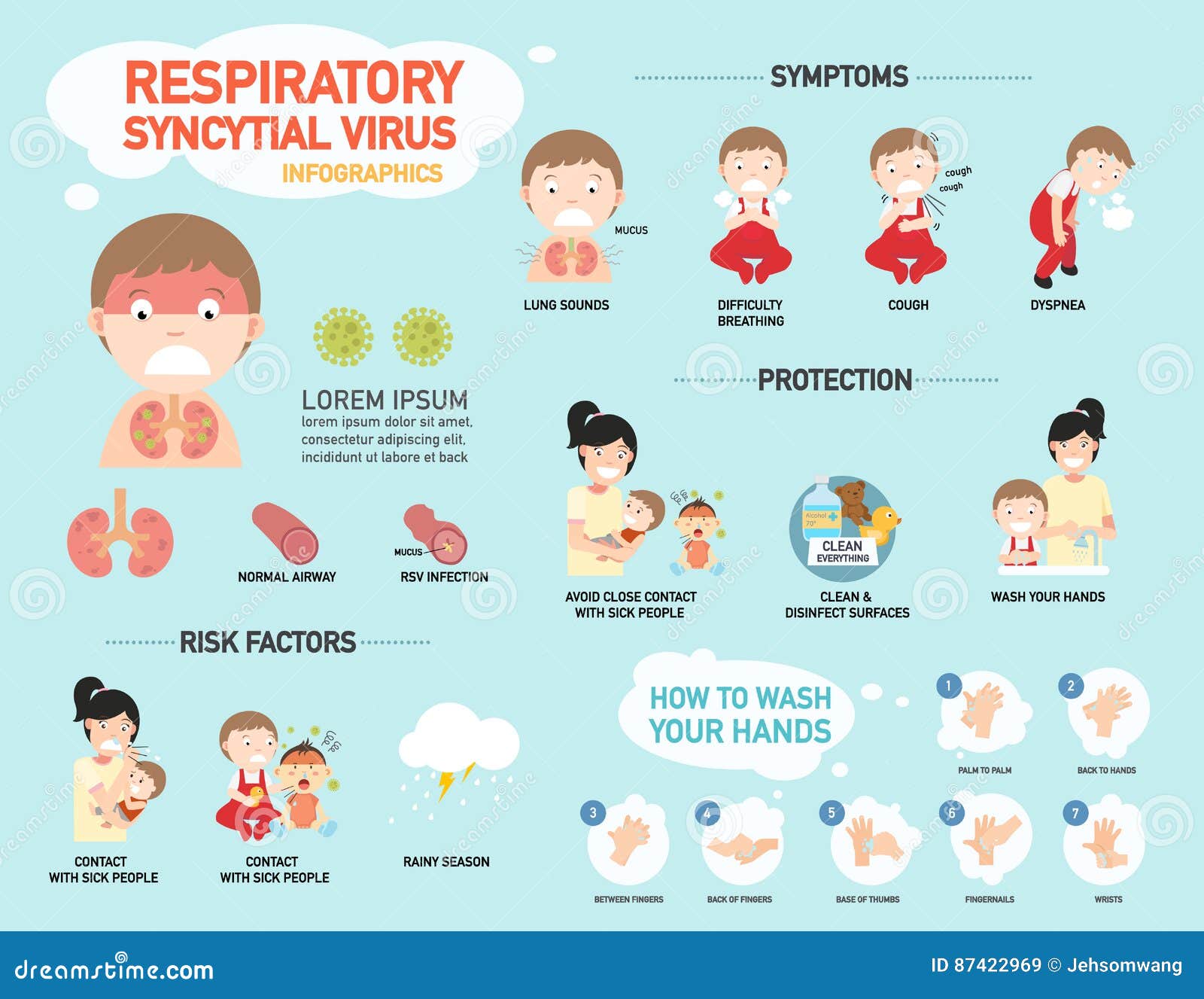
RSV,Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infographic,illustration. Cartoon - Source cartoondealer.com
There is no specific treatment for RSV infection. Treatment is supportive and includes measures to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. These measures may include rest, fluids, pain relievers, and bronchodilators. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. Prevention of RSV infection is important, especially for infants and young children. The most effective way to prevent RSV infection is to avoid contact with people who are infected. Other preventive measures include washing hands frequently, covering coughs and sneezes, and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces.
RSV infection is a serious illness that can cause significant morbidity and mortality in infants and young children. Prevention of RSV infection is important, and there are several effective preventive measures that can be taken. Treatment of RSV infection is supportive and includes measures to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
Table 1: Summary of RSV Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
| Symptom | Prevention | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | Avoid contact with infected people | Rest |
| Cough | Wash hands frequently | Fluids |
| Wheezing | Cover coughs and sneezes | Pain relievers |
| Difficulty breathing | Disinfect frequently touched surfaces | Bronchodilators |
| Decreased appetite | Hospitalization (in severe cases) |



