Ultrasound Vs. X-Ray: Comparative Imaging Techniques For Medical Diagnosis Imaging techniques make it possible for medical professionals to visualize the inside of the human body without making any incisions. Two of the most frequently used imaging techniques are ultrasound and X-ray. While both of these techniques can produce images of the inside of the body, they work in different ways and have different advantages and disadvantages.
Editor's Notes: Ultrasound Vs. X-Ray: Comparative Imaging Techniques For Medical Diagnosis have published 10th June'23. Imaging plays a significant role in the field of medical diagnosis to identify the root cause of the patient's medical issue so that doctors can provide the correct treatment plan.
Our team has done extensive research and analyzed the possible way we could make it easy to understand how Ultrasound Vs. X-Ray: Comparative Imaging Techniques For Medical Diagnosis techniques used for medical diagnosis. The following guide will help our target audience understand the difference between ultrasound and X-ray and to know which technique is right for a particular medical condition.
Key Differences
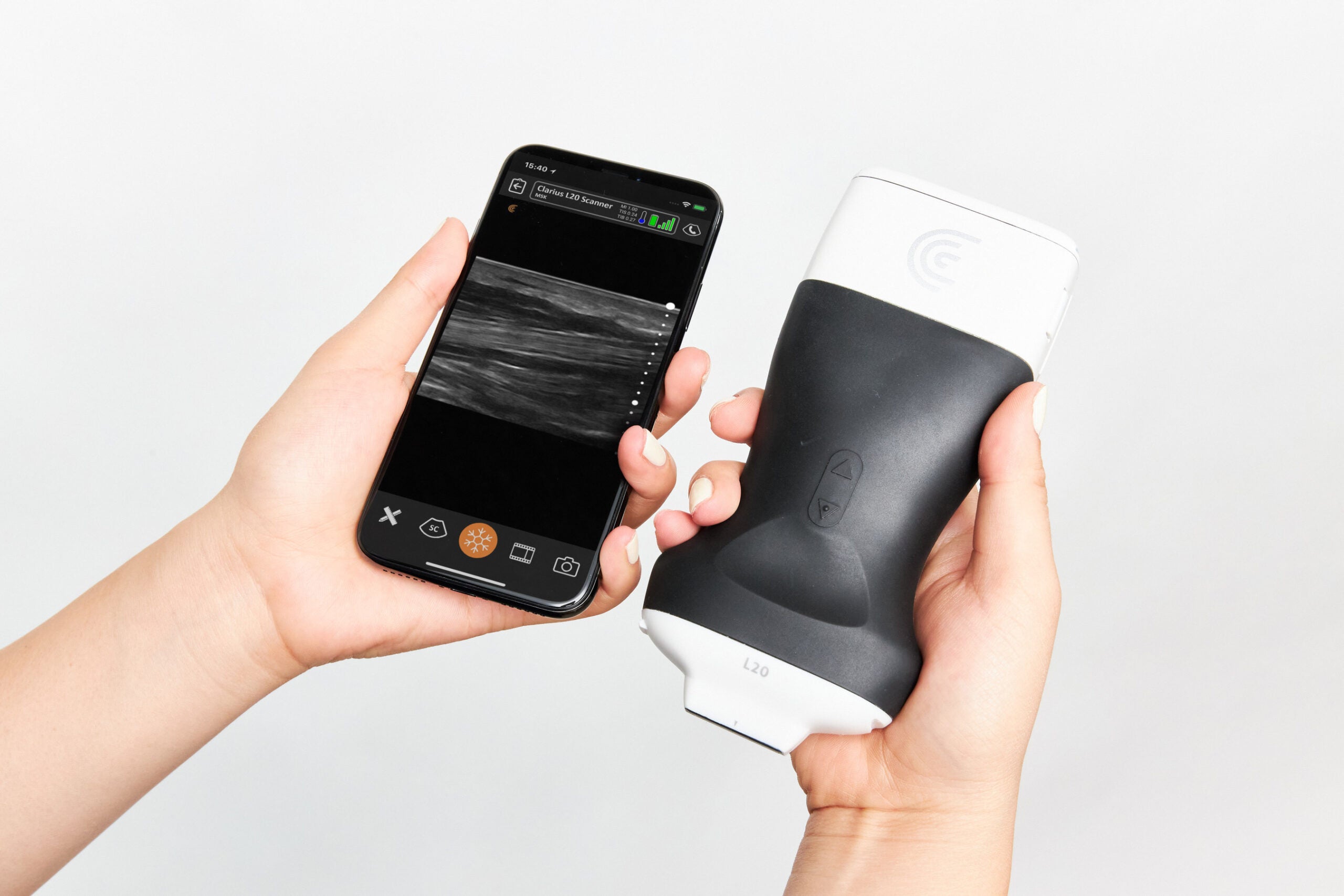

Clarius introduces the world's first ultra-high frequency handheld - Source www.nsmedicaldevices.com
The following table outlines the key differences between ultrasound and X-ray:
Transition to main article topics
FAQs on Ultrasound vs. X-Ray
Ultrasound and X-ray are two common medical imaging techniques that provide valuable information for diagnosing and treating medical conditions. Each technique has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of which technique to use depends on the specific clinical question being asked.

Medical Imaging Techniques For Medical Body Diagnostics Outline Diagram - Source cartoondealer.com
Question 1: What are the key differences between ultrasound and X-ray?
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body, while X-ray uses ionizing radiation to create images. Ultrasound is non-invasive and does not use radiation, making it safe for use in pregnant women and children. X-ray is more invasive and uses radiation, but it can provide more detailed images of bones and certain other structures.
Question 2: When is ultrasound preferred over X-ray?
Ultrasound is preferred when imaging soft tissues, such as organs, muscles, and blood vessels. It is also preferred when imaging the fetus during pregnancy. X-ray is preferred when imaging bones, such as those in the skull, chest, and abdomen.
Question 3: When is X-ray preferred over ultrasound?
X-ray is preferred when imaging bones, such as those in the skull, chest, and abdomen. It is also preferred when imaging certain other structures, such as the lungs and sinuses.
Question 4: Are there any risks associated with ultrasound or X-ray?
Ultrasound is generally considered to be safe, with no known risks. X-ray uses ionizing radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer. However, the risk of cancer from a single X-ray is very small.
Question 5: Which technique is more expensive, ultrasound or X-ray?
Ultrasound is generally more expensive than X-ray. The cost of an ultrasound can vary depending on the type of ultrasound being performed and the location of the facility.
Question 6: Which technique is more widely available, ultrasound or X-ray?
X-ray is more widely available than ultrasound. X-ray machines are found in most hospitals, clinics, and imaging centers. Ultrasound machines are not as widely available, but they are becoming more common.
In conclusion, ultrasound and X-ray are two valuable medical imaging techniques that provide complementary information for diagnosing and treating medical conditions. The choice of which technique to use depends on the specific clinical question being asked.
To learn more about ultrasound and X-ray, visit the following resources:
Tips by Ultrasound Vs. X-Ray: Comparative Imaging Techniques For Medical Diagnosis
Ultrasound and X-ray are two common imaging techniques used in medical diagnosis. They both have their own advantages and disadvantages and are used in different situations.
Ultrasound | MIC Medical Imaging - Source www.mic.ca
Tip 1: Understand the differences between ultrasound and X-ray.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create an image of the inside of the body, while X-ray uses radiation. Ultrasound is typically used to look at soft tissues, such as muscles and organs, while X-ray is typically used to look at bones.
Tip 2: Consider the cost of ultrasound and X-ray.
Ultrasound is typically less expensive than X-ray.
Tip 3: Know the limitations of ultrasound and X-ray.
Ultrasound is not as good at penetrating bone as X-ray, so it cannot be used to look at structures that are deep inside the body. X-ray, on the other hand, can penetrate bone but it cannot provide as much detail as ultrasound.
Tip 4: Be aware of the risks of ultrasound and X-ray.
Ultrasound is generally considered to be safe, but it can cause some discomfort. X-ray uses radiation, which can be harmful if it is not used properly.
Tip 5: Choose the right imaging technique for your needs.
The best imaging technique for you will depend on your specific needs. Your doctor can help you decide which technique is right for you.
Ultrasound and X-ray are both valuable imaging techniques that can be used to diagnose a wide variety of medical conditions. By understanding the differences between these two techniques, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Ultrasound Vs. X-Ray: Comparative Imaging Techniques For Medical Diagnosis
Ultrasound and X-rays are two widely used medical imaging techniques that provide valuable information for diagnosing a range of medical conditions. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on the specific clinical question being asked.
- Principle: Ultrasound uses sound waves, while X-rays use electromagnetic radiation.
- Real-time imaging: Ultrasound allows for real-time imaging, while X-rays do not.
- Safety: Ultrasound is generally considered safer than X-rays, as it does not involve ionizing radiation.
- Cost: Ultrasound is typically less expensive than X-rays.
- Portability: Ultrasound machines are more portable than X-ray machines, making them more suitable for use in remote or resource-limited settings.
- Specificity: X-rays are more specific for detecting certain types of abnormalities, such as bone fractures and calcifications, while ultrasound is better for visualizing soft tissues.
In conclusion, the choice between ultrasound and X-rays for medical diagnosis depends on several factors, including the specific clinical question being asked, the patient's condition, and the availability of resources. Ultrasound is a versatile and relatively safe imaging technique that provides real-time imaging and is well-suited for examining soft tissues. X-rays are more specific for detecting certain types of abnormalities and are often used to assess bone health. Both techniques play an important role in modern medical imaging and can provide valuable information for diagnosing and managing a wide range of medical conditions.
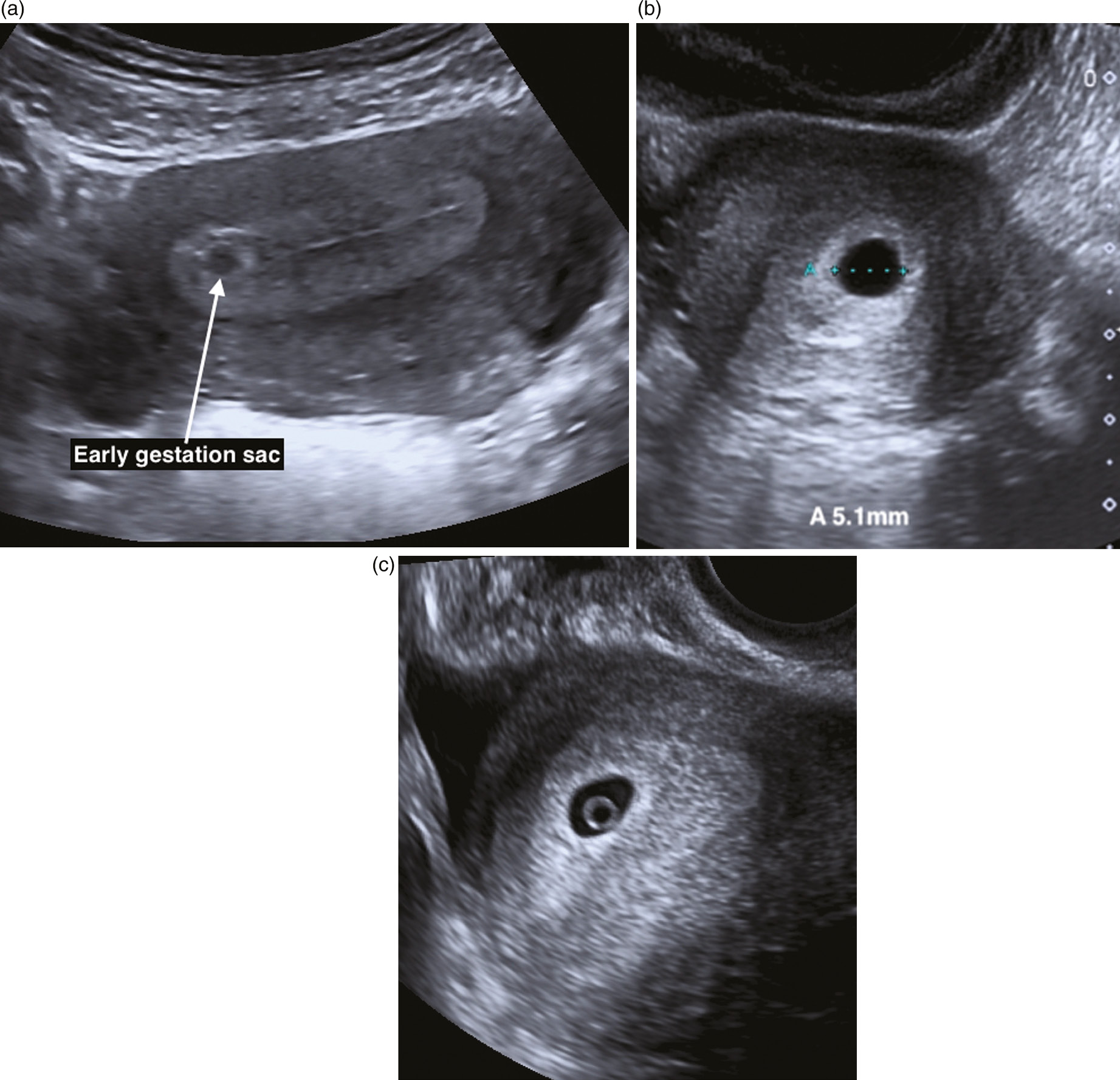
Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasound Vs Normal Pregnancy - Source inutoneko.info

Conventional ultrasound findings in chronic liver disease | Radiology Key - Source radiologykey.com
Ultrasound Vs. X-Ray: Comparative Imaging Techniques For Medical Diagnosis
Ultrasound and X-ray are two widely used medical imaging techniques that provide valuable information for diagnosing and treating medical conditions. While both techniques offer unique advantages, fully understanding the distinction between ultrasound and X-rays is essential for healthcare professionals and patients to make knowledgeable decisions about the most appropriate imaging method for specific diagnostic needs. This article will explore the connection between ultrasound and X-ray, comparing their imaging techniques and highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages to facilitate informed decision-making in medical diagnosis.

Which medical imaging technique? - Source education.theiet.org
Ultrasound and X-ray imaging techniques differ significantly. Ultrasound utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal body structures. The sound waves are emitted by a transducer, which is then placed on the skin's surface. It generates real-time images of internal organs, tissues, and blood flow. X-ray, on the other hand, employs electromagnetic radiation to create images of the body's internal structures. An X-ray machine emits a beam of X-rays that passes through the body, capturing images of bones and other dense tissues on a special film or detector. The resulting images are static and two-dimensional.
Each imaging technique has distinct advantages and disadvantages. Ultrasound is particularly useful for visualizing soft tissues and organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys. It is also commonly used for prenatal imaging, as it is safe for both the mother and the developing fetus. X-ray, on the other hand, is well-suited for imaging bones and detecting fractures, tumors, or other abnormalities in bone structures. It is also widely used in pulmonary imaging, chest X-rays being a common diagnostic tool for respiratory conditions like pneumonia or tuberculosis.
In conclusion, both ultrasound and X-ray are valuable medical imaging techniques that complement each other in providing comprehensive diagnostic information. Understanding the advantages and limitations of each technique empowers healthcare professionals and patients to make informed decisions about the most appropriate imaging method for specific medical conditions. By harnessing the unique capabilities of ultrasound and X-ray, medical professionals can effectively diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions, leading to improved patient outcomes and overall healthcare quality.
The comparative table below provides a concise overview of the key distinctions between ultrasound and X-ray, further illustrating their respective strengths and weaknesses:
| Characteristic | Ultrasound | X-Ray |
|---|---|---|
| Imaging Technique | High-frequency sound waves | Electromagnetic radiation |
| Real-Time Imaging | Yes | No |
| Penetration Depth | Limited (soft tissues) | High (bones and dense tissues) |
| Safety for Pregnancy | Yes | No (potential harm to developing fetus) |
| Applications | Soft tissues, organs, blood flow imaging | Bones, fractures, chest imaging |



